 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Internal
oxidation in silver and platinum alloys
|
 |
 |
 |
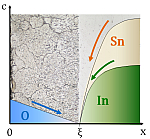
Internal
oxidation is a diffusion controlled solid-state reaction involving a
noble matrix element and a less noble alloying element.
Oxygen diffuses into the alloy and reacts with the less noble element.
Internal oxidation is widely applied for dispersing
fine oxide particles homogeneously in noble metals such as silver,
platinum, nickel and copper. In silver alloys internal oxidation is
utilized to minimize the contact erosion of silver contact materials in
electrical contactors and for dispersion hardening of the metal matrix.
The hardening effect is due to interactions of finely dispersed
ceramic particles with dislocations during plastic deformation. The
strength of the material is thus retained up to temperatures close to
the melting point. In the case of platinum alloys, considerable
strength of an oxide dispersion strengthened material allows for
application temperatures up to 1600°C, i.e. near the
melting point of
pure platinum.
The mechanism of the nucleation of oxide particles in
silver and platinum is investigated in collaboration with industrial
research and development laboratories. |

|
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
Exudation
of the noble alloy component during internal oxidation
|
 |
 |
 |
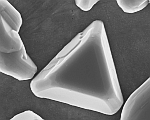
| One
aspect of the internal oxidation is the atomic diffusion of one or
several noble alloy components against the moving direction of the
internal oxidation front towards the sample surface. Crystallites of
the noble elements nucleate at grain boundaries and at the sample
surface, in some alloys to a degree that they conjoin to pure metal
layers. As a result pure internal and external metal
layers reduce
locally the dispersion hardening effect. A study on the
driving
force and kinetics of the formation of the pure metal layers is in
progress. |

|
|
 |
 |







